单词查找树
单词查找树是一种已知字符集的字符串查找树, 读作"try".
初始状态
假定字符集为{x, y, z}, 节点相应位置为0表示绝对没有以其结尾的字符串.
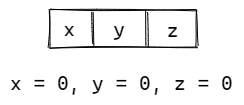
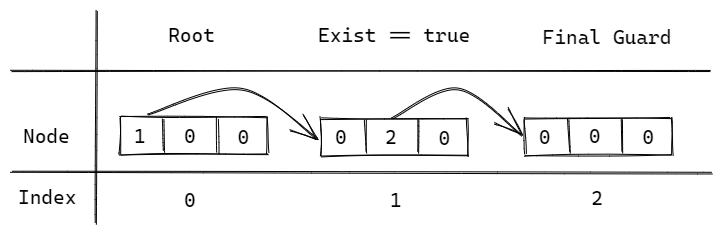
填充状态
现在的状态是插入字符串xy后的状态, 叶子节点一定是一个全空节点, 作为最后的守卫.
该表示法通过索引值表示链接关系, 展开后就是一个度为字符集大小的查找树.
具体实现
class Trie {
private:
vector<array<int, 26>> nodes;
vector<bool> exist;
vector<int> tags; // 维护存在性之外的状态.
int size = 0;
public:
Trie() : nodes(1), exist(1), tags(1) {}
void insert(const string &str) {
int current = 0;
for (char c : str) {
c -= 'a';
if (c < 0 || c >= 26) {
throw runtime_error("@1: invalid character");
}
if (current == nodes.size()) {
nodes.emplace_back();
}
if (nodes[current][c] == 0) {
nodes[current][c] = ++size; // 链接到下一个节点.
}
current = nodes[current][c];
}
// 补齐叶子节点.
nodes.resize(current + 1);
exist.resize(current + 1);
tags.resize(current + 1);
exist[current] = true;
}
int find(const string &str) {
int current = 0;
for (char c : str) {
c -= 'a';
if (c < 0 || c >= 26) {
throw runtime_error("@2: invalid character");
}
if (nodes[current][c] == 0) {
return 0; // 找到了叶子节点.
}
current = nodes[current][c];
}
return getTag(current);
}
private:
static const int UNUSED = 0;
static const int USED = 1;
int getTag(int pos) {
if (!exist[pos]) {
return 0;
}
if (tags[pos] == UNUSED) {
tags[pos] = USED;
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
};
这里只针对ACM使用场景简单实现了少了API, 另外将节点单独封装成一个单独的类会是一个不错的改进!